The expression contains elements like:
- Muscular strength
- Endurance
- Condition
- Movements (Co-ordination)
- Speed
- Nourishment
In this part I shall concentrate about muscle strength. The other elements are or will be described on other pages.
Why physical training?
It is well known that
exercise is healthy, and by moving the body you receive some kind of physical training.
But you can also give the training a purposeful meaning.
Physical training
has that purpose to give the player a better basis to use his/her technical abilities
The physical state of training is decisive for how hard, how long, how fast,
how high etc something can be done.
What happens by
physical training?
When you start with physical training the body
will be influenced. It will be worn down (gets tired), but afterwards it will build
itself up in order to be better prepared for the strain. The greater strain and
intensity the more the organism is influenced and that means, that the more you
train the better the body will be to cope with the strain.
However this
demands that there are periods between the training where the body can rest and
restore its health. When the body has rested and is ready again, an interesting phase
occurs - the super compensation phase. Under this phase the body is receptive for
doing a little extra.
The training can be viewed as divided into some
phases:
|
1 |
The training |
|
2 |
Restitution |
|
3 |
Super compensation |
|
4 |
Return to the starting point |
The last mentioned point is a very unpleasant phase for the athlete. A whole
year can be spent with intensive training and a season can end with a top condition.
Then a good summer vacation is held, where the greatest activity is to bring lunch
packs and sun lotion to the beach, and the body will incredibly fast return to the
starting point, and the whole year of training will be lost. It is therefore important
that the athlete also during the summer vacation does some training and not stops
completely
One have to decide which form of training to be used.
Continuous training
This form included only phase 1 and 2.
The restitution period overlap the super compensation period and no improving of
the form is achieved, as the next training pass happens after the super compensation
period.
The continuous training can also be performed by not trying to improve
oneself in the super compensation period but just be happy of the fact that one
is not so tired as before.
Form improving training
Here phase 1, 2 and 3 is used. First training, then restitution and then training
again under the super compensation period, where the goal is to make the things
faster, more times, heavier or whatever the goal of the training might be.
It is important to be aware of the possibility that the form improving training
does not end in a wearing down training instead. It is important that the body has
time to restitute before the next training pass. If not the performance will be more
and more poor.
When are you in the super compensation period?
It depends very much on the type of training and may vary between 24 and 72 hours.
If strength or explosive training is the goal, the resting period will typically
be 72 hours.
What is included in physical training?
The
answer is: All kinds of physical activity.
Under physical activity the muscles are used, their strength is used, the condition
and the movements are used (co-ordination).
Before you - as trainer -
evolve a breathtaking training program, you must consider what is to be improved
as well as what age and sex, your players have. In general the following is determining
the training
- Age and sex
- The level of training
- The common state of
training
- The knowledge to the exercises
- The demands of the sport
-
The purpose with the training
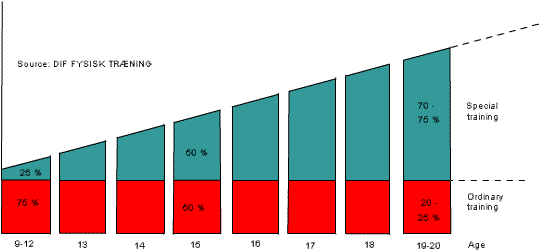
|
PHASE 1 Movement pattern and coarse motor function. Basic technique in special athletics. Games and basic training. All-round training. (Lots of movements) Alternating training and interesting training. |
PHASE II Many-sided training. Partial special training but not forced.
|
PHASE III Sensible planning of games/competitions.
|
Top performances |
Especially in connection with youth players attention must be put on the fact
that they are different than grown-ups. The bones are softer because to lesser content
of chalk, the density of the muscles is smaller and the abilities of the muscles
are different. This is the reason why youth are more exposed to injuries caused
by overtax and especially just before and right after the heavy growth in
the of puberty there are a very great risk of injuries, injuries who in worst case
might be permanent.
It is important to perform exercises for all muscle
groups in order that the body does not become crooked. That's why the exercises
must be made "to both sides". If a right-handed player always practice the jump
on left leg it only takes a little imagination to visualize a "Pop-Eye" left leg
and a sickly looking right leg. Further more the player must learn to perform the
exercise correctly in order to avoid injuries or other unsuitable things.
Before all physical training it is important to be well warmed-up. Besides that
you must always put technique-, speed and co-ordination exercises before the more
exhausting exercises like strength- and endurance exercises, because a worn out
player is more exposed to injuries. Finally the player must stretch out.
The choice of strain
Up to 13 years:
All-round training
of strength by using light strain, for instance medicine balls, bars, ribs and jumps
with the players own body weight as load. NO TRAINING WITH WEIGHTS!!!
14-17
years
Under this age there are favourable conditions for development of
agility and explosive strength, and agility training can be used with great advantage.
The training of strength must still only be used with the players own body weight as
load, but controlled training with small weights can now be used (it must be possible
to perform an exercise 20-30 times). This type of training must not include elements
where the full strength must be used and all the time consideration must be taken
to the players bodyweight, sex and background.
17-18 years
Explosive
strength training may now be the goal and training of pure strength can in this
age group be performed with even light strain.
Belly bending
Especially belly bending in connection with female players (both youth and senior)
has been debated many times and there are 2 different opinions. It is possible to
get a panel of experts who will state that it is harmfulness for them to do belly
bending., but it is also possible to get another panel of experts who states that
there is no danger. I have chosen to let the players have the benefit of the doubt
and do not let them have hundreds of belly bendings, but only a reasonable few,
performed by just let the upper body raise a couple of centimeters from the ground.
Further more exercises with powerful bendings backwards must be avoided
As woman naturally have a greater natural mobility, the risk of injuries is greater
in connection with physical strain and consideration the this must be taken.
Mental training under physical training
I have said to
my players that they - while training at home - must have a goal. If a player is
able to make 15 push-ups as basic training the player must perform all 15 each time.
If the player feels that there is room for a couple more push-ups, she/he must be
aware, that all the following training must include the extra push-ups and if that
is a problem, they must fight for them. Everything else is quitting. .
Here the difficult part lies - to force oneself and not give in. It is easy to
think " I can't be bothered with this any more". In fact you are able to do much
more than you think. Imagine that 2 identical players are hanging in the arms in
a bar. One of the players feet are 10 cm over the floor and the other players feet
are hanging 10 cm over a pool with ice cold water. I am sure that the player
hanging over the floor drops down first.
The cold pool and the trainer has
the same role in this situation. Both make the player do a little bit more. However
even a trainer is not able to make the athlete do the absolute top effort. I remember
a Karate-lesson, where the whole team was lying on the floor performing belly bending.
I cannot remember how many hundred bendings we had made, but at last the whole team
war mourning and informed the trainer, that it was impossible to do one more. We
were totally worn out. "All right" said the Sensei. "Stand up!" The team stood up
and the Sensei could inform us, that he noted that we rose by bending the upper
body up to a sitting position and we owed him at least one more belly bending. We
came down again and made a couple extra.
Further advantages
by physical training
Besides improving speed, strength and endurance it has
been proven at an essential advantage will be achieved by using sensible
arranged physical
Niels Wedderkopp (Odense University 1996) has made an investigation based on 16-18 years old handball players. The investigation showed that players - especially the woman - have many and serious injuries especially in knees and feet and that 50 per cent of the injuries happened without physical contact with another player. As a part of the investigation some of the players received a special training program and in this group the injuries were greatly reduced (90 per cent) in relation to the other group, who had just been training in the usual way. The number of injuries in the investigation group was only 23 per cent in the special group. This means that the injuries can be reduced by 77 per cent. Worth thinking about! The investigation also showed that just by focusing on the injury problem a reduction of 50 percent was achieved in the whole control group.
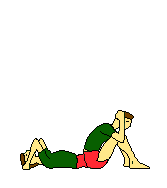
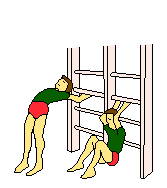
EXAMPLES OF TRAINING EXERCISES
 |
 |
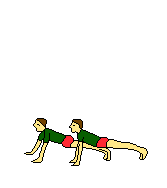 |
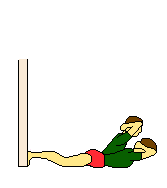 |
|
| Own weight | Own weight | Own weight | Own weight | |
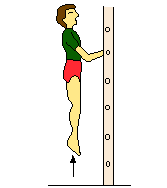 |
||||
| Own weight | ||||
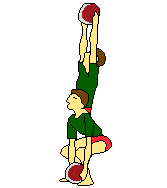 |
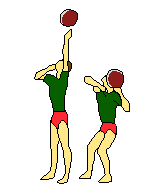 |
 |
 |
|
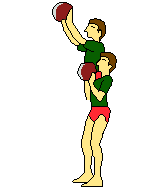
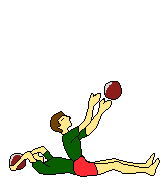
| Medicine ball | Medicine ball | Medicine ball | Medicine ball | |
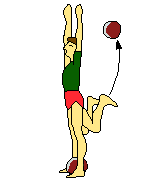 |
||||
| Medicine ball | ||||
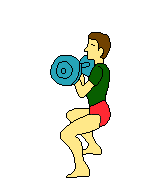 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Weights | Weights | Weights | Weights | |
 |
||||
| Weights |