Learning is a relative permanent change of a person's conduct as consequence
of experience and training.
But even the best trainer cannot teach a player
anything if certain conditions are not present.
The conditions are:
-
The player is motivated i.e. likes the sport, is interested in the sport and
wants to learn the sport
- can understand and interpret the meaning with
the exercises and information (also called perception)
- is able to remember
the exercises and information and don't forget at once
A player, who
in principle hates handball, but attend handball because, for example, the father
was a handball player once, will have great difficulty in learning anything.
In addition to this, the maturity has a great role and there is a big difference
between children and adult's understanding of a training situation. The adult
can see and accept that some boring exercises must be made before the full play
will work. The children will play here and now, and training exercises which
do not contain shooting at goal or likewise are boring. This does however not
mean, that the children cannot learn the basic, but they must be taught in an
entertaining way and in small doses.
MOTIVATION
Motivation is fundamental for all learning. No motivation - no learning. But
what is a player's motivation to play handball? This can be divided into the
outer- and the inner motivation. The outer motivation could be to the wish to
make a trainer, parents or teammates happy - the inner motives could be the
joy of the activity in the sport.
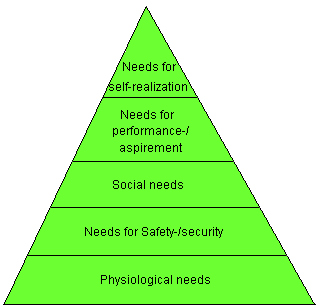
Maslov's pyramid of need can show these
motives:
As examples can be mentioned:
- a talented player with special training
and great attention from the coach stops playing, because her best friend moves
to another team or stops in the club.
Her social need is therefore greater
than her need of achievement.
If you look at the pyramid:
Need of self-realization:
- to realize one's self
-
create activity
- inner experiences
- to set a goal
- to develop
- create
- experiment
Need of performance/aspirement:
- experience one's own distinctive character
- independence
- competence
- has status
- to protect own identity
The Social
need:
- the society
- member of a team
- contact with others
Need of security and safety:
- safety in the situation
- security arrangements
- security during sickness
- economical security
- trust in given promises
Physiological needs
- hygiene
- movement
- sex
- to have enough to eat
- to sleep peacefully
PERCEPTION
Perception is the player's ability to
receive and adapt information about one self and the surrounding world.
These
impressions are received by
- Sight -> the visual impression
- Hearing
-> the auditory impression
- Feeling -> the kinetic impression
But
the players adapt the impressions differently as earlier experiences and especially
the selecting factor has influence on the total impression.
Especially about
the selecting factor it can be said, that it constitutes the fact, that the
player has preferred one impression instead of another. Some players focus a
lot on their opponents and what they do - others focus on the ball - they have
chosen 2 different factors as being the one on which they concentrate
There is also a difference in the way the player uses her senses. Some understand
an exercise best by looking at others performing it; others must try the exercise
in order to learn it. Some must have a careful explanation before they can perform
the exercise. An example could be a cross where 1st crossing player consistent
just runs past the 2nd crossing player and passes the ball. A visual or explaining
method must therefore be used to make the 1st player start running against the
defense in order to move it before passing the ball.
An old Chinese proverb
says:
"What I hear, I forget!"
"What I see, I remember!"
"What I do,
I understand!"
THE MEMORY
The memory is the ability
to remember the different things, which have been practiced. The motivation
and the learning principles, which have been used during training, again affect
it. The more engaged and motivated the better memory becomes Therefore a player,
who has worked with problem solutions and analyzing of errors will remember
the exercise better that one who just perform it.
Unfortunately the memory
is not a lasting thing and if the things are not repeated they will soon be
forgotten and only a little part will remain of what has been learned.
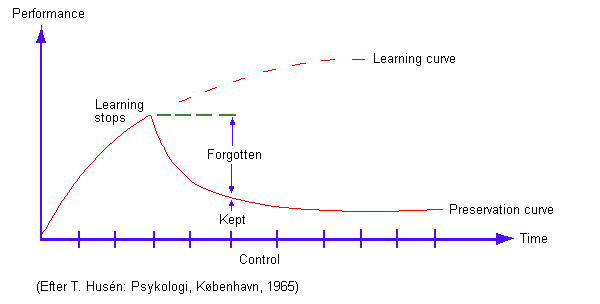
Especially it is bad with the verbal abilities. Here the things will be
forgotten very fast, but in return the rest will be remembered for a long time.
OVER LEARNING
The more a certain ability is practiced
the longer it is remembered. Things, which have been done for a very long time,
i.e. bicycling and swimming, won't be forgotten even if many years have passed
since last practiced. Therefore over learning is much used in sport to make sure,
that the many skills are remembered and remains in a high quality
THINGS WHICH MAY IMPROVE THE MOTIVATION, PERCEPTION AND BY
THIS THE QUALITY
THE QUALITY
The training
itself must be interesting for the player. By this the player becomes more motivated
to do the things right, and thereby reduce errors, the speed and precision improves.
If at the same time you inform the players that their skills will be tested,
you obtain a better learning of the motor abilities, and they are better
remembered. Never start a new exercise just after another new exercise has been trained.
You get a negative effect against the previous exercise and it will soon be
forgotten.
THE REWARD
Remember to tell the players
that they are doing well. Players, both young and old like attention, and by
telling them that they are doing something will you get their attention. The
worst you can do is to overlook a player, who makes a great effort to obtain
your praise.
FEEDBACK
It is of great importance
to be told at once whether something is right or wrong. It is of no use to go
through a training session later and inform, what was good and/or bad. It must
be said during the exercise. However a video can be used, but it must be used
to show the team's whole effort. With new exercises it is important to give feedback
often, whereas it is not so important during the over learning phase.
PRAISE OR WHIPPING
Always choose praise or positive criticism.
It has no positive effect to yell to a player, that now she must start running
instead of walking. Instead tell her easy and calmly that she ought to speed
up if she wants to learn the exercise correctly. Drop the remark: "Come
again!" It is often heard in games and often taken negatively = "Do the same
mistake again??" Instead tell the player why she didn't succeed and inform her
of the means to do it correctly and send her out in the game again.
The worst
you can do is to ignore the players. The learning effect grows low, as the motivation
drops.
THE BODY LANGUAGE
The body
language is more informative than verbal sentences. When a player is in contact
with her trainer, 55 per cent of what the trainer sends out is body
language, 38 per cent is the tone of the voice and the last 7 per cent are
what is actually
said. If a trainer leans back with crossed arms and a sullen face, a very clear
signal is sent out: "I don't care to use any more time and effort on you anymore!"
An engaged trainer shows with waving arms and positive remarks that he is just
as much playing the game as the players
A trainer can also take advantage
in learning the players' body language and take action on an earlier moment
TIPS IN LEARNING
1. Create motivation before action.
2. Analyze the exercises to create a positive transfer.
3. Demonstrate the
correct way to do the exercise.
4. Use many ways of teaching.
5. Spread
out instead of gathering the training.
6. Help the players to evaluate their
own movements and performance.
7. Use our body language - it talks all the
time.
8. Make sure that the players are corrected at once if they are doing
wrong movements or actions.
9. Praise just as much as you correct.
10.
Create context between goal and actions.