To co-ordinate ones basic movements is inborn and reflexlike. A new born child learns very fast to get hold on to something, but leading the arm against the thing, the child will hold is at start very groping, but quickly more and more surely. The child quickly learns to crawl, which in fact demands an incredible amount of co-ordinated movements and very soon the child is running around.
Think about how many co-ordinated movements it takes just to run. Without going into the small details you must stand with the feet a little apart. Now the body is leaned forward and left foot is lifted by bending the knee a little and the foot is put forward. At the same time the toes and foot of the right leg is pushed hard against the ground and the knee is also used to get extra force, making a jump forward. At the same time the right arm is moved backwards and left arm forward. Remember to bend the elbows. The toes makes the last push just before the jump. Now you land on the left leg with the knee slightly bend and the foot flexed to receive the bump while landing and so on... .
Rather complicated, but because of years of "training" it is a simple thing for an 8-year old player. Most of the movements are controlled by the central nerve system and the child don't think about how the movements must be made - it just do it. And one day the sports becomes interesting and new movements must be learned, which are not known to the central nerve system.
But when a player must learn to receive a ball while running, perform one or more dribbles, catch the ball again, take 3 steps and shoot with the correct foot in front - then a lot of new movements must be learned and co-ordinated and it is extreme difficult for a beginner. It is of no use to ask a beginner to do all this at once. The exercise must be divided into parts (catch, dribble, 3-step approach, shooting with the correct foot in front) and when all part elements are mastered, the parts can be put more and more together, until the full exercise is performed. First learn to stand, then walk and then run.
The training of co-ordination with children up to 15 years must be a major part in the training, as the central nerve system is maturing between the age of 8 to 15 years and all-round training in co-ordination can result in a broad range of motor programs and movement patterns. Thorough work through of the exercises with be stored in the central nerve system and after that the exercise can be performed without any actual control of the exercise
Certain things are so well learned, that they can be difficult to change or do otherwise. The sign for "substitution" where you perform circles with your hands and the circles follows the same direction is easy to perform. The fingers can also follow each other quite easily. But try to start with your fingers pointing at each other under your chin and then let one hand move in a circle outwards and downwards and the other hand downwards and inwards and continue making circles. Most people will find that very difficult and the body and mind will get into a fiercely battle of what to do and what is actually done.
The purpose with training in co-ordination is to automate a number of accidents and optimize those - that is make them as expedient as possible. The training in co-ordination can therefore be well placed in the sports, where well-defined movement patterns (athletics, swimming, gymnastics, trampoline jump) are used. However the training also has effect in the more "open" sports and the principles of the training of co-ordination has got a new meaning in learning systems in team-ball-sports. The attack-systems in handball are build upon fast muscle movements in connection with a fast observation (sense perception) followed up by a total, arranged sequence which include many part elements, which have been automated.
The co-ordination exercises must include balance, feeling of rhythm, ability to react, space orientation, eye-hand and eye-foot co-ordination and muscular tension regulation and the more muscles who are involved in an event, the more focus must be put tin the training of the co-ordination.
Some handball coaches choose to let their players train only piston movements - maybe in order to get a here and now result - but by learning the players in the puberty more all-round movement pattern it will cause that a later learning of new movements becomes more easy. A good co-ordination will in terms result in a better rhythm when playing together, change of direction, feints and acceleration.
Training of co-ordination
When co-ordination is trained it is an advantage to build on things, which are natural for the players and take advantage of that. For instance you can build on the reflex-like defending mechanism when something is thrown against one self. A ball is thrown against a player and the first reaction from the player is to raise the arms to prevent the ball hitting the face or body. Nor start working with the same reflex, but with focus on the correct way to hold the hands in a catching position instead. Then sliding forward and throw the ball back. A player who is impossible for the others to catch while playing "catch each other" because his/her ability to change direction has a natural ability to perform very good feints in handball.
The training is divided into phases::
The orientation
The athlete is informed about what is to be worked with - either verbally or by having the sequence shown.
The gross co-ordination
Here the fundamental movements in the exercise is trained. It is an advantage to let the players perform the exercise in the wrong way and then in the correct way in order to make the difference visible. Dependent of the complexity of the exercise, the total method, where the full movement is practised or the part method, where the single elements of the exercise is practised, can be used.
The fine co-ordination
Here the part method is used, where every single movement of the exercise is practised and eventual new elements are put into action. It is a condition that the whole movement of the exercise is known by the players before this point. Quite young players do no benefit of the fine co-ordination as their abilities are not fully developed.
The automation
The automation is done by repeating the exercise again and again, until it is a natural thing for the players to do. It is very important that errors are corrected while doing this, as errors, which have been automated are very difficult to correct. Further more the exercise must be performed with optimal speed, corresponding to the requirements in a game situation. An automated slow attack system will be performed slowly in a game - an automated fast attack system will be performed fast
Stabilization//Adaptation
Here small adjustments to the automated is performed, as increased strength, agility and technique also has a role.
Mental co-ordination training
A part of the central nerve system is called "the association center". This center is active just before the execution of a well-known combined movement. If the player has decided to make a sequence of movements, a "picture" appears just before the execution. Then the movements are performed in accordance with that "picture".
However it is not necessarily that a movement is known and automated. It is also possible to imagine a movement pattern and by this activate the center. This can then be used and is called mental co-ordination training
'
New stuff is difficult and must be learned at a slow speed at first. By this a "picture" is drawn in the association center and when the exercise becomes more and more sure and fast, the "picture" will be correspondingly developed. As it is the senses who develops the "picture", it will also be the senses who tells the player, when the exercise is in accordance with the "picture". It feels right. The player can then increase the speed, and the senses will tell if it still feels correct or what must be changed in order to match the "picture". It is also possible for the player to put new details into the "picture" and concentrate on those to feel, if they fit into the "picture" - that means to feel if the new details don't spoil the total "picture
During time the player will have gathered a large number of "pictures". When the player works in a "picture" and suddenly meet an obstacle, which prevents the "picture" to be completed, the "picture" can be replaced by another, which is a continuation of the old one, but includes the new situation.
Transfer of learning
When an exercise is learned, it will have influence on the learning of new abilities - especially exercises which is like the previous. The learned will be transferred to the new and this can be done in two quite different ways:
Positive transfer
It becomes more easy to learn the new and the difference is of such a kind, that it is easily acquired.
Negative transfer
The new stuff is learned more slowly, as the difference is of such a kind, that it conflicts with the previous learned. .
No transfer
If the new stuff is quite different from the learned, there is no transfer.
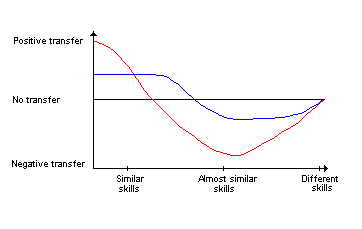
The drawing shows, that under a high level of automation a positive transfer will occur with exercises very close to each other, but under a low level of automation a negative transfer will occur. That means that the higher the level of automation is the greater the likeness between the exercises must be to obtain a positive transfer.
Reversed a high level of automation will create a negative transfer, if the exercises are somewhat different. The difference can be difficult to learn because if feels wrong, and the automation will "force" the player to do the exercise in "the old way". .
In general you should not train exercises, which are too much alike in the same training lesson, but distribute the exercises among several days. That prevents the possibility that the player mix the things together, but makes the player able to let the single exercise stick in his/her memory.